Creating a Playful Path: Activities That Foster Early Childhood Development
Key Takeaways:
- Engagement in playful activities nurtures young children’s cognitive, social, and emotional development.
- Incorporating sensory play can stimulate brain development and support learning new skills.
- Parents and educators can create enriching play environments without expensive resources.
- BalancingIt’s structured learning with free play is essential to foster creativity and problem-solving skills.
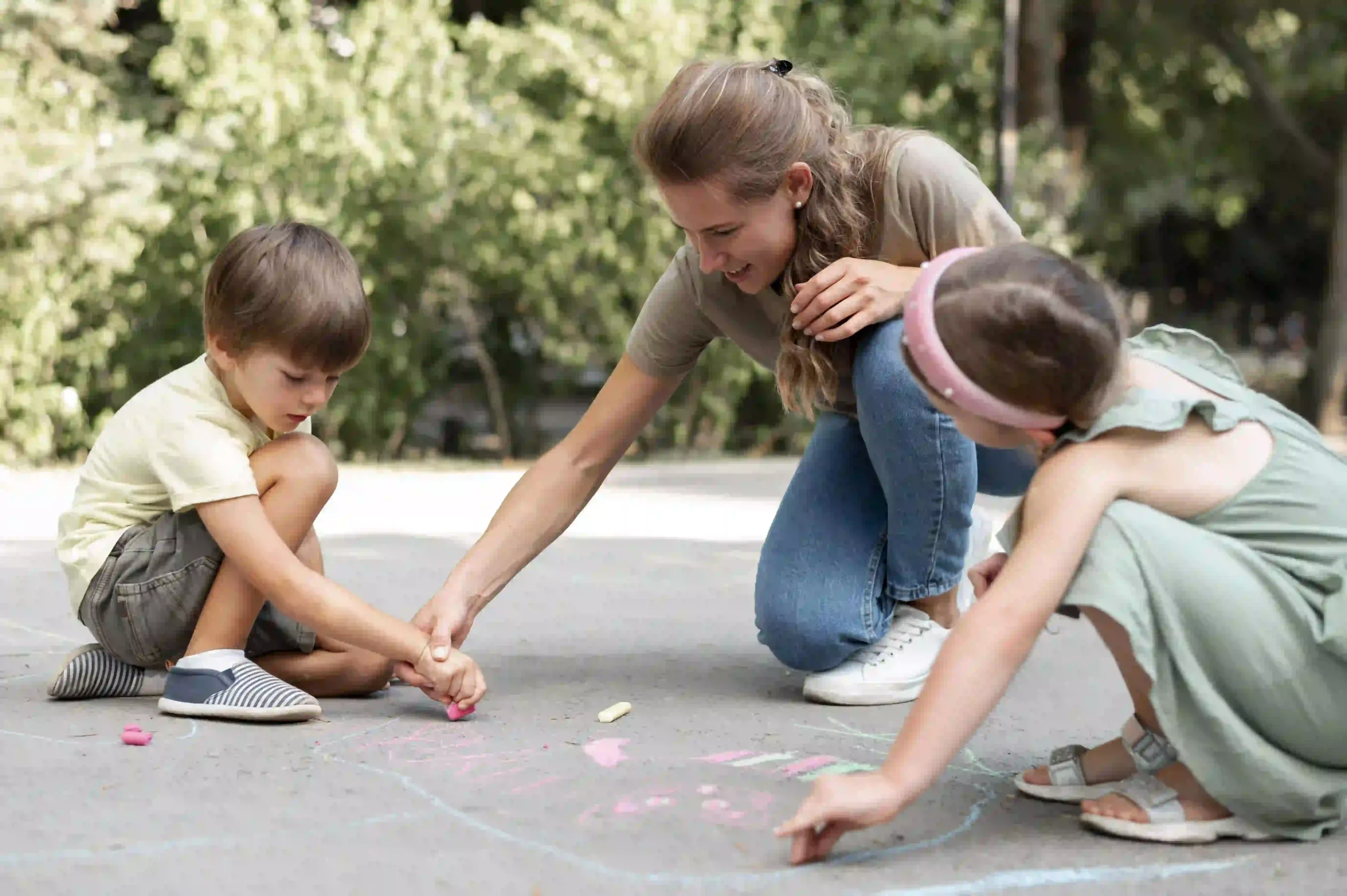
The Role of Play in Child Development
Play is more than just an enjoyable pastime for children; it is an essential mechanism through which they make sense of the world surrounding them. Playing helps children process experiences and develop a deeper understanding of their environment. Preschool board games offer structured avenues for children to develop problem-solving skills and the ability to strategize and make decisions, mimicking real-life situations in a safe and supportive setting. This engagement fosters neural development as children’s brains form new connections critical for their overall cognitive growth. Additionally, play provides emotional benefits by allowing children to express their feelings, build self-confidence, and develop resilience through trial and error.
Engaging Activities for Cognitive Growth
Cognitive development during preschool forms the basis for a child’s ability to think effectively and learn efficiently. Engaging children in puzzles or sorting games can significantly amplify their cognitive skills. Such activities introduce the concepts of sequencing, categorization, and cause and effect in a tangible and relatable manner for young minds. According to research on early childhood education, these types of activities not only help improve concentration but also enhance language and communication skills. They help children understand how to follow instructions and the importance of patience, persistence, and precision. By challenging themselves to solve problems, children learn the value of effort and experience the satisfaction of achievement firsthand.
Social Skills Through Group Play
Social skills are critical to overall child development and essential for healthy relationships. Group play is an excellent opportunity for children to acquire these skills in a practical setting. Through group dynamics, children learn to communicate effectively, resolve conflicts amicably, and recognize the importance of empathy by understanding others’ perspectives and feelings. As children engage in team activities, they learn to negotiate differences, collaborate towards common goals, and celebrate collective achievements. These interactions not only build communication skills but also bolster self-esteem and teamwork. The experience of working together fosters a sense of belonging and community, aiding children in understanding their roles and responsibilities within a group.
Incorporating Sensory Experiences
Sensory experiences hold the key to unlocking numerous developmental benefits for children. When engaging in activities such as playing with clay, water, or rice, children stimulate a range of sensory receptors, enhancing their brain’s ability to process diverse types of sensory input. Sensory play supports the development of motor skills, whether gross or refined, and builds cognitive frameworks through exploration and discovery. These activities also provide therapeutic benefits, often as a calming method that helps children manage stress and emotional tension. Sensory play’s tactile and interactive nature encourages children to design, construct, and experiment, promoting creativity and innovation while reinforcing neural pathways essential for learning and development.
Practical Tips for Creating Enriching Play Environments
Enriching play environments is critical for engaging children in meaningful, intentional learning experiences. Crafting such environments needn’t be expensive or complex; the most effective tools are often simple household items that can be repurposed creatively. Items like cardboard boxes, fabric scraps, and kitchen utensils can be used to design open-ended play scenarios that stimulate imagination and adaptability. Introducing children to a mix of physical, cognitive, and artistic activities fosters a multi-dimensional approach to learning, catering to various interests and intelligences. Parents and educators can enhance these environments through diverse and inclusive play materials that challenge and intrigue children, sparking curiosity and promoting lifelong learning habits.
Balancing Structured and Free Play
Achieving a proper harmony between structured activities and free play is vital for a child’s overall development. Structured play, such as organized sports or guided educational activities, ensures that specific skill sets are developed efficiently. These activities introduce discipline, order, and technique in a guided fashion. However, free play allows children to use their imagination and make their own choices, teaching them independence and encouraging creative problem-solving. Some experts suggest that free play can be a natural extension of structured learning, where children can apply and experiment with newly acquired skills in innovative and personal ways. Balancing these approaches nurtures a flexible learning environment that can adjust to the child’s changing needs and preferences.
Technology and Play: Finding the Right Balance
The rise of technology presents both opportunities and challenges in children’s development. While the digital world offers interactive educational tools that can engage children in new ways, it is imperative to manage screen time to avoid hindering physical activity and face-to-face social interaction. Thoughtfully integrating technology into play can enhance creative learning and provide exposure to digital literacy. However, it should complement other experiential and tactile play rather than replace them. Carefully chosen digital applications can support structured learning objectives, while traditional play ensures the development of critical physical and social skills necessary for well-rounded growth.
Real-Life Examples of Play-Based Learning
Real-life examples illustrate the profound benefits and versatility of play-based learning. Taking children on exploratory walks in nature can nurture a deeper understanding of ecosystems while inciting curiosity and awe. Such experiences allow children to engage directly with their surroundings, fostering observational skills and environmental appreciation. Meanwhile, collaborative art projects stimulate both individual expression and community interaction. These projects encourage children to explore color, form, and function concepts, cultivating aesthetic sensibility alongside creativity. These play-based activities strengthen cognitive, social, and emotional development, equipping children with many skills that serve them throughout their educational journey. By embedding learning within play, educators and parents can holistically nurture a child’s development, preparing them for future challenges and triumphs.













Post Comment